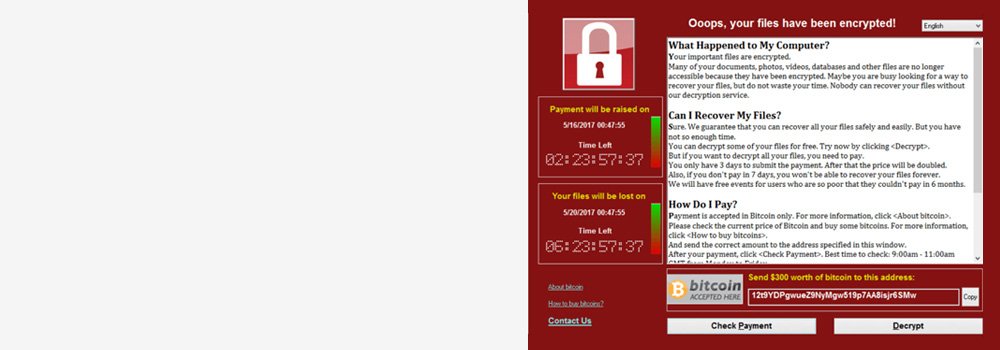
Ransomware Data Recovery Services
Sheffield Data Recovery provides end-to-end, forensic-grade recovery for ransomware-impacted laptops, desktops, external drives, NAS/RAID and virtualised servers. We operate strictly read-only on originals, preserve evidence, and pursue all viable decryption and non-decryption recovery paths (snapshots, replicas, unencrypted remnants, application caches, cloud versions, etc.). We support UK-wide incidents (including Plymouth) for organisations and individuals.
How to submit media: place affected drives in an anti-static bag, cushion in a padded envelope or small box, include your contact details, and post or drop off. Diagnostics are free; we confirm scope and options before work.
Incident-Safe, Forensic Workflow (What We Actually Do)
-
Containment & Chain-of-Custody – isolate hosts/storage; capture logs; document artefacts; image originals with hardware write-blockers.
-
Threat Family Identification – sample encrypted files, ransom notes, extension patterns, mutex/registry keys; static/dynamic malware triage to classify strain/variant.
-
Media Imaging Strategy – PC-3000/DeepSpar imagers with unstable-media profiles; head/zone prioritisation (HDD), namespace cloning (NVMe), and RAID member cloning before any virtual rebuild.
-
Key Material Hunts – memory dumps (where feasible), disk artefacts, config blobs, key vaults; AD/EFS/DPAPI recovery material; KMS logs; hypervisor snapshots.
-
Parallel Recovery Tracks – (a) Decryption track (keys, decryptors, flaws), (b) Data-recovery track (snapshots, unencrypted copies, carving, app-level repairs), (c) Rebuild track (RAID/VM/container reconstruction).
-
Verification & Packaging – test-decrypt on samples, hash-verify output (SHA-256), open-file checks (DB consistency, video index repair, PST integrity), report of evidence and recovered data.
50 Technical Techniques We Use for Ransomware Decryption & Data Recovery
Note: “Decryption” paths aim to recover keys or use safe decryptors; non-decryption paths salvage usable data without keys. We pursue both in parallel to maximise outcomes.
-
Variant Fingerprinting & Config Extraction – parse ransom note/extension, YARA signatures, embedded config to reveal crypto scheme (e.g., AES-CTR + RSA-OAEP, ChaCha20+RSA, Salsa20), C2 URIs, campaign IDs.
-
Known-Decryptor Matching – test against vetted decryptors (where available) for families with public keys or leaked master keys; run on isolated clones, never originals.
-
Session Key Recovery from Memory – capture RAM (if still available) to extract symmetric keys, RSA private keys, or DPAPI master keys left by the malware or OS crypto subsystems.
-
DPAPI/LSA Secrets Recovery – dump DPAPI master keys and system/LSA secrets to unlock user/EFS keys required for decrypting files that ransomware re-wrapped with OS crypto.
-
Active Directory EFS Recovery Agents – recover domain EFS recovery certs to unlock EFS-encrypted content that was secondarily impacted.
-
Partial/Intermittent Encryption Exploitation – identify “every Nth block”/header-only encryption; reconstruct large file types (VMs, videos, archives) using intact regions plus format-aware repair.
-
Known-Plaintext Testing for Stream Modes – for CTR/stream ciphers with predictable headers (ZIP/JPEG/OOXML), test-derive keystream fragments and recover segments.
-
Weak PRNG/Nonce Collisions – detect IV/nonce reuse across files to recover keystream or mount related-key attacks for select flawed families.
-
Faulty RSA Implementation Checks – assess RSA modulus patterns for small prime reuse or CRT leakage; if found, factor and derive private keys (rare but case-winning).
-
Configuration Mistakes (Embedded Private Keys) – scan samples for embedded operator keys or debug builds with hard-coded secrets.
-
Shadow Copy Harvesting (VSS) – enumerate and mount Volume Shadow Copies that survive; export historical, unencrypted versions.
-
Windows Previous Versions & System Restore – pull file history where ransomware failed to purge or where endpoints were offline during purge.
-
Hypervisor Snapshots (ESXi/Hyper-V) – recover from datastore snapshots/checkpoints; reconstruct VM disks even when guest OS is encrypted.
-
Array-Side Snapshots (SAN/NAS) – vendor snapshot/clone recovery (NetApp, Synology, QNAP, Dell/HP) to roll back shares/LUNs without keys.
-
Cloud Object Versioning – OneDrive/SharePoint/Dropbox/Google Drive: version restore, tenant-level rewinds, API-driven selective rollback.
-
Backup Set Extraction – Veeam/Commvault/Acronis/CrashPlan repositories: index and restore clean points; undelete from GFS chains/immutability stores.
-
WAL/Journal Reconciliation (DBs) – for SQLite/Jet/NTFS journals and database WAL files not encrypted due to locks; merge into rebuilds.
-
PST/OST & Mailbox Cache Salvage – recover cached mailbox data; rebuild indices; export to new PSTs.
-
Application Cache & Proxy Media – Lightroom catalogs, FCPX/Adobe Premiere proxies, thumbnails—recover originals/proxies to salvage working deliverables.
-
File Carving with Format Repair – carve JPEG/RAW/HEIC, MOV/MP4/MKV, DOCX/PDF from unallocated space; repair headers, moov atoms, xref tables.
-
Transaction-Log Time Slicing – replay filesystem logs up to just before encryption event to recover consistent file states.
-
USN Journal & MFT Timelines – correlate file creation/rename/encrypt events; identify files that remained untouched and carve their prior content.
-
Fail-Open Shares & Offline Caches – harvest Offline Files (CSC) and SMB client caches left unencrypted.
-
Deduplication Stores – Windows Server Dedup chunks often survive; reconstruct files using chunk hashes and metadata databases.
-
Email/Document Server Drafts – recover autosave/draft copies (Office autorecovery, temp files) that were open during encryption and escaped.
-
RAID Virtualisation Before Decrypt – safe virtual RAID rebuild (0/1/5/6/10) from cloned members to ensure integrity before any decrypt attempts.
-
NAS-Specific Recoveries – QNAP/Synology/Asustor: recover from snapshots, hidden @eaDir, recycle/previous versions, and LVM/mdadm layers.
-
ESXi/VMFS Flat Disk Stitching – reconstruct VMDK from descriptor + flat files; salvage guest files from within.
-
Sparse/Thin Provision Fix-ups – correct provision metadata to mount virtual disks with partially encrypted blocks.
-
Selective Decrypt & Test Harness – decrypt representative samples per file type; validate via hash/open tests before batch operations.
-
Header-Only Repair for Media – rebuild MP4/MOV moov indexes, MKV cues, ProRes/CinemaDNG clip structures after partial block encryption.
-
Archive Directory Rebuild – reconstruct ZIP central directory/7z headers using local headers to rescue intact entries.
-
Compound Document Repairs – fix OOXML ZIP structures and OLE containers to open Office files post-partial decryption.
-
Filesystem Meta Rebuild (APFS/HFS+/NTFS/EXT/XFS/ReFS/ZFS) – repair catalogs, object maps, B-trees, bitmaps; graft orphans to recover trees even alongside encrypted siblings.
-
Cross-Host Differential Analysis – compare encrypted host vs. peer not yet encrypted to recover common data from peer caches/syncs.
-
Cold Storage/Offline Media Ingest – restore from tape, WORM and offline HDDs unaffected by outbreak.
-
C2 Sinkhole Intel (When Lawful) – use threat intel on seized servers/leaked keys to validate decrypt feasibility for specific campaigns.
-
Key Derivation From Ransom Notes – some families encode victim-specific IDs that, combined with local artefacts, derive session keys.
-
Mistimed Kill-Switch/Abort Flags – exploit logic bugs where encryption halts mid-file, leaving reconstructable tails/heads.
-
File Pair Analysis – use known original versions (emailed/previous exports) to infer keystream segments for partially encrypted siblings.
-
Malware Sandbox Replay – safely detonate on lab images to extract live keys/configs; never on originals/production.
-
Driver Hook Reversal – remove malicious filter drivers that block access to survivors; mount volumes cleanly for export.
-
Boot Record/Loader Repair – restore boot and partition metadata (GPT/MBR/EFI) when ransomware sabotages boot to coerce payment.
-
Credential/Key Recovery from HSM/TPM/BitLocker – recover encrypted data protected by OS crypto where ransomware changed ACLs but not keys (requires valid creds/recovery keys).
-
Process Hollowing Artefact Recovery – dump hollowed processes to harvest transient keys/configs.
-
Network Share Journal Pulls – leverage SMB server journals and backup logs to reconstruct last-known-good file versions.
-
Immutable Object Stores – MinIO/S3-compatible buckets with retention: enumerate legal hold objects; restore pre-attack.
-
Email & Collaboration Restores – M365/Google Workspace admin-level versioning/restore beyond user UI limits.
-
Timeline-Constrained Carving – carve only sectors written before the encryption start timestamp to avoid encrypted noise.
-
Operator Negotiation & Proof-of-Life Validation – where a client chooses to negotiate, we validate decryptor on samples, sandbox runtime, and pre-stage rollback to avoid secondary damage. (We never advise payment; we technically validate client-direct choices and protect data.)
What We Need From You (If Available)
-
Affected devices (drives/NAS/RAID members) and, if possible, a memory image from an impacted host.
-
Any credentials/keys (BitLocker/FileVault/EFS), backup locations, cloud admin access (for version restores).
-
A copy of the ransom note and any sample encrypted files.
Deliverables
-
Decrypted files or recovered data from non-decryption paths, verified by SHA-256 and sample-open testing.
-
A forensic summary of actions, artefacts, timelines, and recommendations to harden backups/segmentation and prevent recurrence.
Why Sheffield Data Recovery
-
30 years of incident-safe, forensic-grade recoveries across endpoints, servers and storage arrays.
-
Deep filesystem, RAID, hypervisor and backup expertise to maximise outcomes even without decryption keys.
-
Controller-aware handling of HDD/NVMe/SSD media; advanced imaging toolchain; rigorous verification.
Start a Free Diagnostic
Package the media safely (anti-static + padded envelope/small box) and post or drop it in. We’ll assess, present options, and proceed with the recovery path you approve.